The SIR Model on novel coronavirus
Since a deadly virus appears to be spreading across the globe, I thought it would be useful to explore how this spread is modeled mathematically, and make some predictions about how quickly this can grow.
The simplest model of disease spreading starts by breaking a population up into compartments:
- S (Susceptible)
- I (Infected)
- R (Removed️)
Then, the model describes the flow between these compartments.
NOTE: This version of the model works over short periods and ignores births and natural deaths.
The equations to describe these flows are given by these non-linear differential equations, if you haven’t taken calculus, check out the yellow note below the equations to see what these terms mean. The number N is the population size, and an assumption of the model is that S + I + R = N.
$$ \frac{dS}{dt} = -\frac{\beta I S}{N} $$ $$ \frac{dI}{dt} = \frac{\beta I S}{N} - \gamma I $$ $$ \frac{dR}{dt} = \gamma I $$
Crucially, solving differential equations is how we get a prediction out of this model.
One thing to notice right away is that the overall change of S + I + R over time is zero, notice that:
$$ \frac{dS}{dt} + \frac{dI}{dt} + \frac{dR}{dt} = 0 $$
This reflects the simplifying assumption that births and natural deaths are not part of the model. Now that we have a feel for the shape of the model, the flow between the compartments, we can start to estimate the parameters β and γ and then predict how large this thing can get.
The basic reproduction number is related to the model parameters β and γ like so:
$$ R_0 = \frac{\beta}{\gamma} $$
For the COVID-19 virus, the estimate for R0 is anywhere from 1.4 to 6.49, which is a large range. For the purposes in this post, I’ll do a best-case scenario to get the most optimisitic outcome the model will allow.
From the equations, we can see that the R compartment (dead) grows at a rate of γI, so γ is the fatality rate. From the Wikipedia article as of 2020-03-03, the estimate for the γ of COVID-19 is 1% - 3%.
Solving the equations
We can solve the equations with Mathematica’s NDSolve function. To get some concrete predictions, we need to set the parameters using real world values. Using the latest estimates 1 of R0 between 1.4 and 6.49, we calculate the best-case scenario:
Best-case scenario, R0 = 1.4
Using the real values γ = 0.02 (meaning 2% of people infected by the virus die from the disease), and assuming R₀ = 1.4 (meaning for each person infected, they infect an average of 1.4 new people).
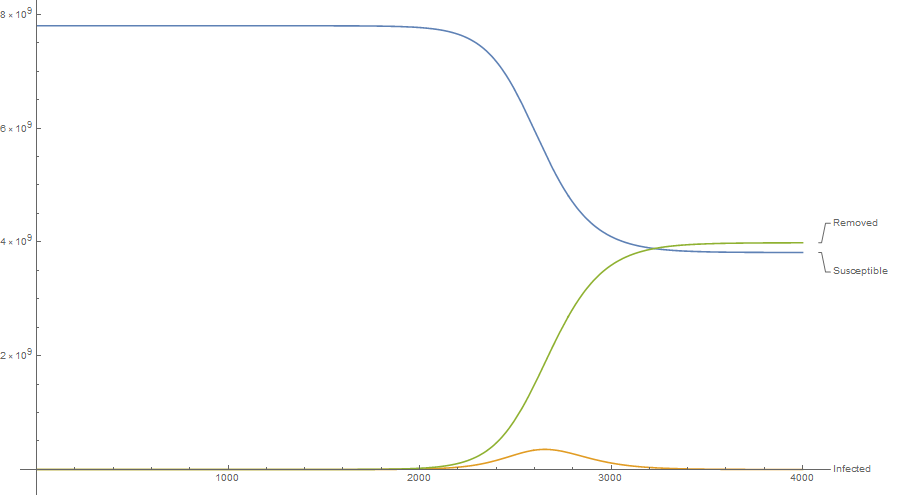
What this model is telling us is that, even under the best-case scenario, if this isn’t contained, it could wipe out half of the Earth’s population. Now, obviously this is just a model, and there are subtleties that are missing, like the window of time when a member of the infected population is actually contagious, and the fatality rate differs based on things like age, health, etc. Another thing this model does is assume people are uniformly intermingling, so this is going to overestimate the outcome, but this is a better approximation of the outcome than just assuming it’s like the flu. As a reminder, flu has γ = 0.001, fully 20 times less than novel coronavirus-19, and kills around 30,000 people per year. Since we don’t yet have a vaccine, or herd immunity, and we already know the fatality rate is at least an order of magnitude larger than flu, we should probably take this seriously.
Worst-case scenario, R0 = 6.49
This graphic was too depressing, so I am leaving it out.
Conclusion
It’s easy to see the current death count of around 3,000 and note that in a world of 7.8 billion people, that’s not so big, but exponential growth defies many of our human intuitions. Infectious diseases can go global really fast if we are not careful. There is precedent, back in the 14th century, the Black Death wiped out between 30%-60% of Europe’s population. Listen to health experts, wash your hands, avoid unnecessary travel, and Don’t Panic.
Citations:
1. Ying Liu, Albert A Gayle, Annelies Wilder-Smith, Joacim Rocklöv, The reproductive number of COVID-19 is higher compared to SARS coronavirus, Journal of Travel Medicine, , taaa021, https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taaa021